Microsoft has shut down more than 1,400 malicious email accounts used by cybercriminals to collect stolen customer passwords via ransomware in the past year. The technology company has presented the second edition of ‘Cyber Signals’, a report that it produces periodically on cyber threats and that shows trends in security and cybercrime. In this issue, it offers insight into the evolution of extortion in cybercrime.
In this analysis, the company highlights that the specialization and consolidation of cybercrime have driven ransomware as a service (RaaS), which has become a dominant business model. RaaS programs, such as Conti or REvil, offer cybercriminals the opportunity to buy access to both ransomware payloads, leaked data and payment infrastructure.
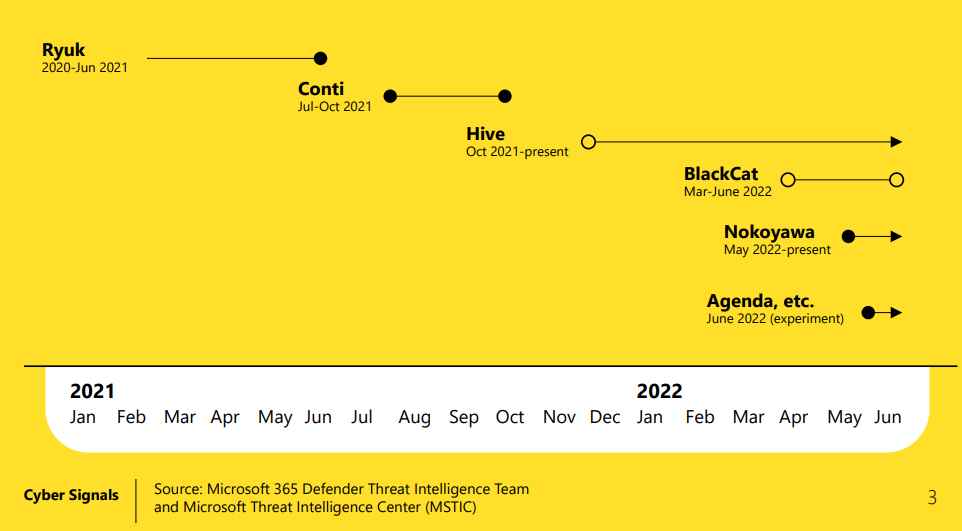
These are used by different malicious actors, among which are the so-called access ‘brokers’, who sell the possibility of accessing the networks. In this way, those cybercriminals who do not have the necessary knowledge to execute the attacks can pay for these techniques and use them.
.
This is what one of the main conclusions of the study refers to, which indicates that companies are experiencing an increase in both the volume and sophistication of attacks. Along these same lines is data offered by the United States Federal Bureau of Investigation, which in its 2021 Internet Crime Report indicated that the cost of cybercrime reached more than 6.9 billion dollars.
Likewise, the European Union information security Agency (ENISA) reported that, between May 2021 and June 2022, ‘ransomware’ threat actors stole about 10 terabytes (TB) of data per month, and that 58.2 percent of stolen files included employee personal information.
On the other hand, Microsoft acknowledges that the majority of ransomware attacks, more than 80 percent, can be traced to common misconfigurations in both software and devices.
This proliferation explains why the Microsoft Digital Crimes Unit removed more than 531,000 URLs and 5,400 phishing kits between July 2021 and June 2022, leading to the closure of more than 1,400 malicious email accounts. The short amount of time that cybercriminals take to access the personal data of a deceived user via email (‘phishing’) is also worrying, since it only takes one hour and twelve minutes to enter their systems.
However, for threats to remote computing devices that communicate across networks or ‘endpoints’, if compromised, the average time for an attacker to start moving within a corporate network is one hour and 42 minutes.
STRENGTHEN DEFENSE IN ORGANIZATIONS
To combat the rise of ‘ransomware’, Microsoft reports that new levels of collaboration are required, in order for more information to be shared between those companies that belong to the public sector and those corresponding to the private sector.
Thus, it is important to build a credential hygiene protocol. This is because cyber attackers use different techniques to progressively spread through a network, seeking logical segmentation of the network based on privileges to limit lateral movement.
It’s also critical to audit credential exposure and for IT security teams and Security Operations Centers (SOCs) to work in a collaborative environment to reduce administrative privileges and have more control over the state of their passwords.
Finally, Microsoft advocates reducing the ‘ransomware’ attack surface and establishing defined rules to mitigate these intruders in the initial stages of infecting computers.

Information security specialist, currently working as risk infrastructure specialist & investigator.
15 years of experience in risk and control process, security audit support, business continuity design and support, workgroup management and information security standards.