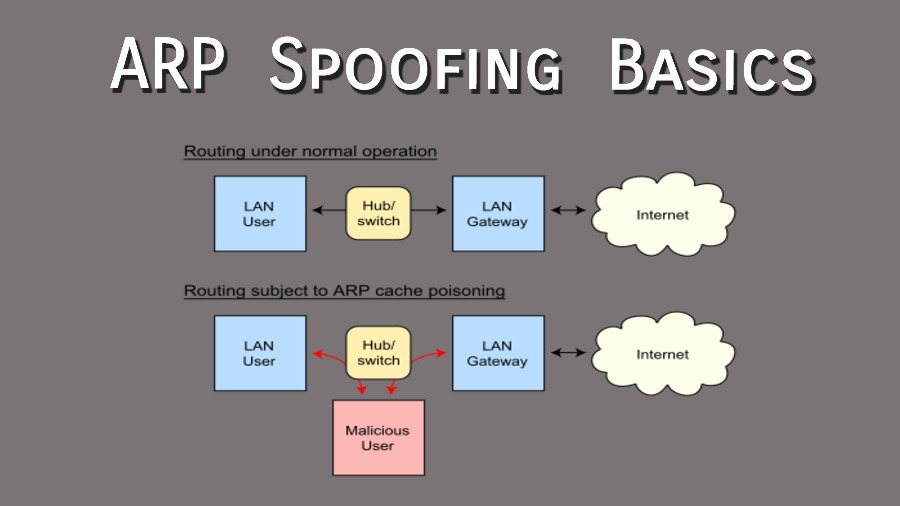
Spoofing is often defined as imitating (something) while exaggerating its characteristic features for comic effect. Not in the real world but also in the computer networking world, spoofing is a common practice among notorious users to intercept data and traffic meant for a particular user.
Though there are a lot of spoofing attacks known in the computer networks world, nonetheless, some of the famous spoofing attacks that are known to almost all of us, with little knowledge in computer networks, are DNS spoofing, IP spoofing, MAC spoofing and even ARP spoofing. Let us know the details about ARP spoofing:
How does ARP spoofing work?
In a broader perspective, ARP spoofing is meant to steal some data intended for the target victim. Here is a series of usual steps that are part of ARP spoofing:
- The attack is usually launched using some tools.
- The attacker opens an ARP spoofing tool such as Arpspoof, Cain & Abel, Arpoison, and Ettercap and sets the IP address of the tool to match the IP subnet of the victim.
- Once the attacker sets the IP address to IP subnet, it starts scanning the whole network to find out the IP address as well as the MAC address of all the hosts on the subnetwork.
- In the next step, a victim is targeted, and the attacker starts sending ARP packet across the Local Area Network (LAN), but the attacker replaces the MAC address of the target with its own MAC address while the IP address remains the same that of a victim.
- As discussed in the previous blog about ARP – the communication at the data link layer happens using the MAC address.
- So, the packets meant for the victim now gets rerouted to the attacker because the MAC address has been spoofed and replaced with the attacker’s MAC address.
- Once the attacker begins getting the packets meant for the victim, it can further launch different attacks.
ARP Spoofing Attacks:
Here is a list of the ARP spoofing attacks that an attacker can launch on the victim:
DOS attack (Denial Of Service)
Denial of Service attack usually involves directing/redirecting too much traffic to a victim to handle. Using ARP spoofing, the attacker associates multiple IP addresses to a single MAC address on a network.
Because of that, the volume of traffic meant for different machines gets redirected to a particular host. The volume of traffic overwhelms the target machine so much so that it gets overloaded and cannot perform other tasks. Read more about DOS attacks.
Man in the Middle Attack
In the Man in the Middle attack, the attacker sits in between the communication that happens between two users. It uses independent connections between two targets giving an illusion to the targets as if they are talking among themselves. Here is a perfect example of this attack given on Wikipedia.
ARP spoofing Detection & Prevention
It is not that these malicious activities cannot be prevented. Here are some of the methods that are employed in ARP spoofing detection and protection:
Authentication & Data Encoding
Authenticating a data sender’s identity in some way can prevent receiving data from a malicious user. Authentication uses credentials from both the systems to authenticate the users.
On top of that, the data is encrypted using some keys by the sender before sending it to the receiver. The encrypted data can only be decoded by some keys which have already been shared by the sender to the receiver beforehand. These things are a part of network security and especially encryption and decryption.
Packet filters
Packet filters are like inspectors which sit and carefully examine all the packets being transmitted across the network. Packet filters are often a part of the firewall programs which keep on looking out for the malicious packets.
For example, a malicious packet could contain packets from outside the network that shows source addresses from inside the network and vice-versa.
Using Static ARP
This is an old school way, but it works well. You manually set up a static ARP for your computers on the subnetwork so that there are no chances of any alterations. However, it is not recommended for a large network because there will a lot of static ARPs, and any small changes will be too much work for the network administrator.
Using VPNs
Using VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) is one of the best ways to get protection against ARP spoofing attack (here are some best VPNs). A Virtual Private Network uses an encrypted tunnel for not only data transmission but also the data that goes through it is encrypted.
Use Anti-ARP Tools
Most of the methods mentioned above either require investment or are not completely failsafe such as Static ARP technique. It can only prevent simple ARP attacks. Some of the ways that Networks admins recommend are using anti-ARP tools to identify and stop the attacker.
Now, here is a little puzzle for you to solve:
Here is a screenshot of my PC below. I found it using “arp -a” command. Based on what you read, can you find what is wrong with the ARP table below?
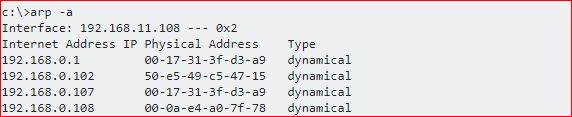
Here is a hint: Look out for the duplicates. Now, based on your finding, can you answer the following questions?
- Who is the attacker here and who is the victim here?
Leave your answers and thoughts in the comment section below. Don’t forget to read our complete coverage on Computer Networks.