Let’s breakdown the little pieces and the critical dots to connect in the perspective of a CISO and a point-of-view from CyberSpace.
The threats and the risks are potentially increasing in Cyber Space and no organization is 100% safe, every CISO should follow the “Zer0-Trust” model over their organization and their security team.
Digital Data isn’t safe anymore after emerging threats due originating from the darknet and
Also Read: Modern CyberSOC – A Brief Implementation Of Building a Collaborative Cyber Security Infrastructure
Let’s have a simple look over the key factors to keep in the mind as a security consultant and as a CISO.
-
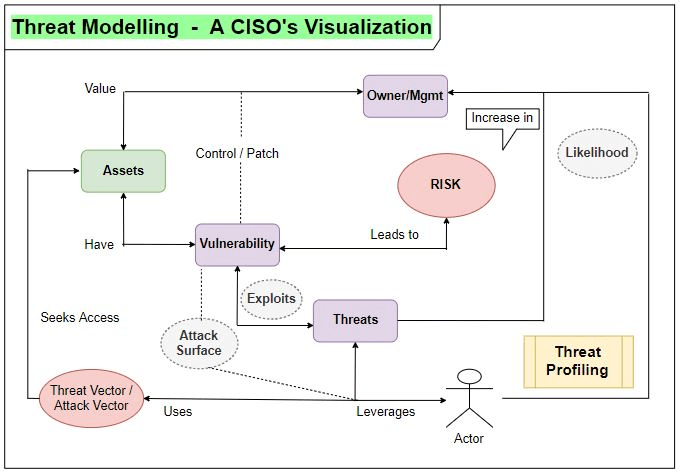
Asset – People, property, and
information. People may include
employees and customers along with other invited persons such as contractors or
guests. Property assets consist of both
tangible and intangible items that can be assigned a value. The digital forms
of data were residing here, most valuable as we are.
-
Vulnerability – A weakness in the IT
infrastructure or its components that may be exploited by a threat to destroy,
damage or compromise an asset. Loopholes or gaps in Application, Network or
even in layouts.
-
Risk – The potential for loss, damage
or destruction of an asset as a result of a threat exploiting a vulnerability.
-
Threat – Anything that can exploit a
vulnerability, intentionally or accidentally, and obtain, damage, or destroy an
asset.
-
Exploit –
breaking the vulnerability, attackers use the existing vulnerability for
their convenient against the owner of the data.
-
Threat Actor/Threat Agent – who
would want to exploit the assets of a company. Maybe an individual or an
organization for any specific causes.
-
Threat Vector/Attack Vector – It’s a
path or means by which a hacker (or cracker) can gain access to a computer or
network server in order to deliver a payload or malicious outcome.
(Phishing/Malware/Drive-by-download/Domain shadowing).
-
Attack Surface – Connecting the multiple
vulnerability dots by an attacker in a specific application or network. Anyone trying to break into a system
generally starts by scanning the target’s attack surface for possible attack
vectors.
- Likelihood – Possibilities of threat actor will carry out a threat.
- Impact – the damage potential, the percentage of loss and the risk factor it made.
- Control – minimize security risks or reducing the exposure of security risks.
- Threat Profiling – Organizations can build with threat intel and various reports and see where they have risk factors based on new emerged threats and profile the threat groups details and coordinate with incident management teams to be precautions. Identifying vulnerable assets & quantifying risk factors of their own assets and map them with possible attack phases. [To understand, who are my threats?]
- Threat Modelling – A process by which potential threats, such as structural vulnerabilities can be identified, enumerated, and prioritized – all from a hypothetical attacker’s point of view. Threat modeling answers questions like “Where are the high-value assets?”, “Where am I most vulnerable to attack?”, “What are the most relevant threats?”, and “Is there an attack vector that might go unnoticed?”. “What can go wrong?” [To understand, what are my threats?]

CISOs and InfoSec teams, should be aware of emerging
threats (whether from the Darknet, or otherwise). Cyber Security is a crucial
component of Information Security, because it is not only concerned with
protecting data, but also concerns protecting the reputation of an organization
and ensuring that its assets are safe and secure.
Cyber Security Teams of an organization must possess
some keyskills, like Red team and blue team excercises, DarkNet Intelligence
and many more.