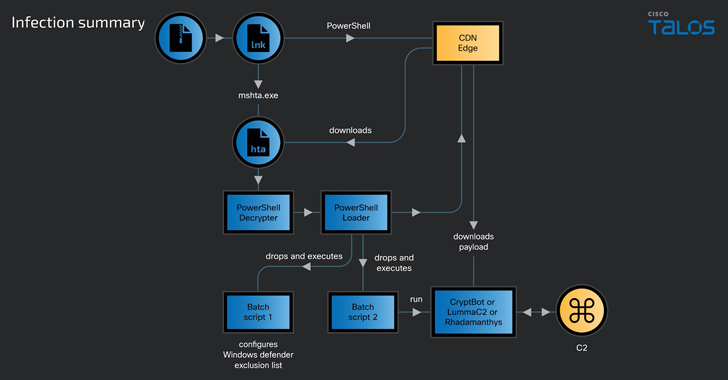
Many researchers believe that this new Trojan could detonate an important wave of cyberattacks
Network security and ethical hacking
researchers from the International Institute of Cyber Security reported the
emergence of a cryptocurrency mining campaign that uses the Linux backdoor
SpeakUp. According to reports, this campaign would have already infected more
than 70k servers worldwide and could have laid the foundation for a massive
botnet.
SpeakUp targets local servers as well as
cloud-hosted machines (such as Amazon Web Services, for example); it is also
believed that it is not only limited to acting on Linux, but it is also capable
of infecting MacOS devices.
The network security specialist Oded Vanunu has
mentioned that this attack extends to servers running ThinkPHP, Hadoop, Oracle
WebLogic, Apache ActiveMQ and Red Hat JBoss. In addition, the specialist
stresses that because this software can be deployed on virtual servers, any
infrastructure in the cloud could also be compromised.
Infection begins when remote code execution
vulnerability is detected (CVE-2018-20062); the code uses command-injection
techniques to load a PHP shell that serves and runs a Perl backdoor.
SpeakUp has a Python script for its spread
whose main functions are to use brute force against administrative panels and
to scan the environment of the infected machine. For this, SpeakUp verifies the
availability of specific ports on servers that share the same internal and
external subnet mask. The idea is to scan and infect the most vulnerable Linux
servers within their internal and external subnets, using a wide range of
exploits.
For its propagation, SpeakUp exploits known
vulnerabilities in six different Linux distros:
- JBoss
enterprise application platform security bypass (CVE-2012-0874) - JBoss
Seam Framework Remote Code Execution Vulnerability (CVE-2010-1871) - Oracle
Fusion Middleware Oracle WebLogic Server Component Vulnerability
(CVE-2018-2894) - Hadoop
YARN ResourceManager command execution exploit - Oracle
WebLogic remote code execution vulnerability (CVE-2017-10271) - Apache
ActiveMQ fileserver file upload vulnerability (CVE-2016-3088)
“Successful exploitation of one of these
vulnerabilities will result in the implementation of the original script on the
exploited server,” the network security experts mention.
The file downloads that the backdoor is showing
are simple cryptocurrency mining scripts; however, SpeakUp authors can download
any kind of code to the servers. Some specialists consider that the injection
of mining code could be a kind of beta test for future hacking activities. “The
threat actor behind this campaign can at any time deploy additional,
potentially more intrusive and offensive payloads. It has the ability to scan
the network of an infected server and distribute malware”, the specialists
concluded.
The first victims of SpeakUp were registered in
Latin America and Asia, although experts consider that the United States could
begin to record the first cases of SpeakUp infection in the coming days.