A new ransomware called Phobos is infecting devices and networks in a massive way
A group of hackers is finding remote access to
networks of different organizations to distribute new variants of ransomware.
According network security and ethical hacking experts from the International
Institute of Cyber Security, attackers are also infecting sites that share cracked
versions of commercial software to spread the ransomware.
Hackers have been remotely accessing enterprise
networks to infect PCs, shared networks and virtual infrastructure with a
ransomware called Phobos, as commented by network
security specialists. In addition, attackers continue to distribute
variants of STOP ransomware through adware embedded in some “cracked software”
sites.
Although many hackers abandoned the use of
ransomware attacks to engage themselves in other malicious activities, such as
the cryptojacking, some cybercriminals gangs continue to dedicate themselves to
distributing encryption software.
ID Ransomware is a platform where victims of ransomware
attacks can identify what kind of malware was used to encrypt their files; it currently
has 673 variants of ransomware identified, a notable increase compared to the
631 variants registered in the platform in the mid-2018.
Among the malware variants identified in ID
Ransomware, there is a new variant of crypto-locker called Phobos, derived from
the Greek term for ‘fear’. Phobos has been attacking multiple organizations
since the beginning of 2019, warn experts in network security, emphasizing that
this malware is very similar to the ransomware Dharma; this ransomware has the
ability to block files on a local drive, as well as mapped network drives,
unmapped network shares, and virtual machine drives.
While some variants of ransomware infect
systems with the help of spam or phishing campaigns, Phobos seeks access to
open or with few security measures RDP ports, according to experts.
Lists of vulnerable RDP ports can be purchased
at low cost in some forums frequented by cybercriminals that try to exploit
these weaknesses with brute force attacks. This means that criminals could
spend weeks, even months, infiltrated into an organization’s networks to infect
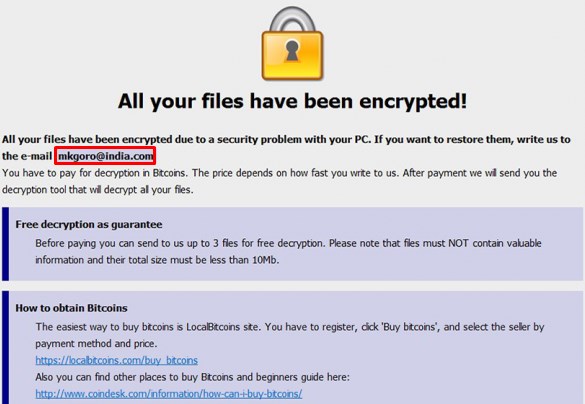
their systems with ransomware. The ransom note that Phobos delivers to the
victims after blocking and encrypting their files is identical to the ransom
note that delivered the ransomware Dharma at the time, because it really only
changes the name of the malware.
In the ransom note even some security services
are offered: “We also offer services. Want to know multiple tips to protect yourself
against these attacks? -The price is 0.1 Bitcoin, and you must remember, our
work is very difficult and requires a lot of time and costs”. At this time, 1
Bitcoin is equivalent to $350 USD.
Network security experts are asking
organizations and individual victims of ransomware to avoid making any payment
for ransom as far as possible, since paying these fees directly finances these
malicious activities.