The massive data leak occurred due to misconfigured cloud services used by Android apps with millions of downloads.
Personal data of over 100 million Android users were exposed due to misconfigured cloud services. The issue was identified in around 23 applications, which boasted up to 10 million downloads and included internal developer resources.
SEE: Warning as hackers breach MFA to target cloud services
The issue was identified by Check Point researchers who wrote in their blog that when configuring/integrating third-party cloud services into apps, it is extremely important to follow best practices.
“By not following best-practices when configuring and integrating third-party cloud-services into applications, millions of users’ private data was exposed,” researchers noted.
Millions of Users Affected
This type of misuse not just impacts the users but also the developers. That’s because users’ personal data is exposed and put at risk, and also at risk are the developers’ internal resources like access to storage and updating mechanism.
As per Check Point’s blog post, the apps were available on Google Play Store. Some of the names they shared include:
- iFax
- T’Leva
- Astro Guru,
- Logo Maker
- Screen Recorder.
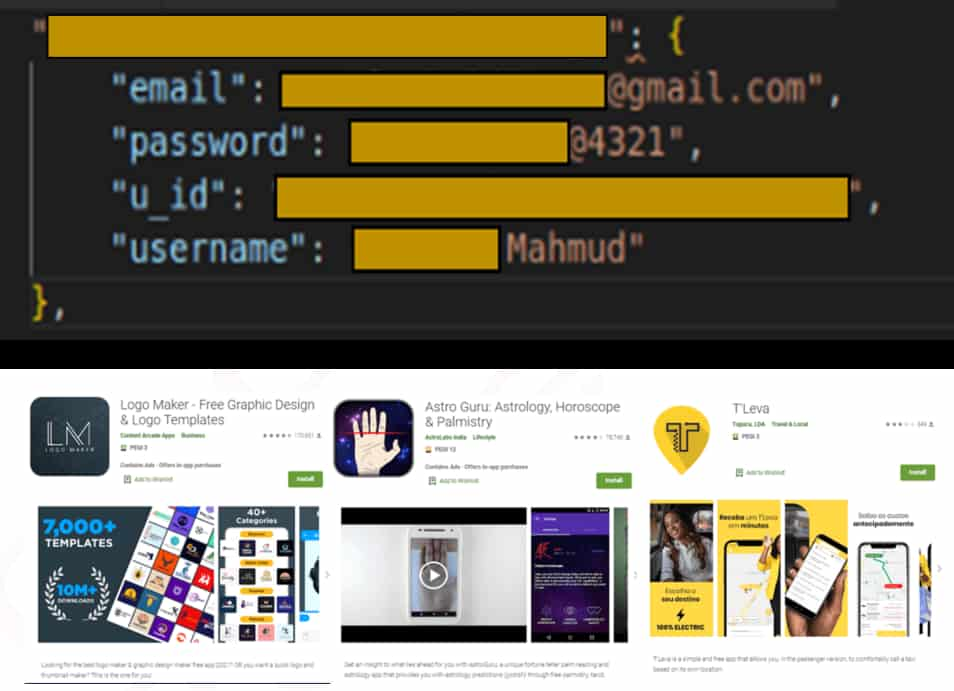
Researchers noted that a password didn’t protect many databases used by app developers to store data on Cloud. Therefore, anyone could access the sensitive, personal information of more than 100 million users, including:
- Names
- Dates of birth
- Location
- Email addresses
- Passwords
- Photos
- Gender
- Chat messages,
- payment details
- Contact information
- Push information, etc.
Sample data:
App Data Leakage- A Largely Underrated Issue
The sheer number of applications having misconfiguration issues indicates a deep-rooted and widespread problem, and cyber crooks can easily leverage such apps to fulfill their nefarious objectives.
Since app developers use real-time databases for data storage in Cloud services and sync it with connected clients in real-time, a slight mistake can cause massive data exposure.
SEE: Chrome on Android will alert, fix compromised password
Check Point researchers could obtain data of those using the Angola-based taxi app T’Leva. They easily accessed messages exchanged between passengers and drivers, along with riders’ full names, destination/pick-up locations, and phone numbers. All this was possible because the database wasn’t secured properly.
Moreover, app developers embedded key needed to send push notifications and access cloud services directly from the app. This could allow cybercriminals/scammers to send a fake notification to users from the developers’ side or redirect users to a phishing page.