TheMoon botnet was first identified in 2014 and it targets exploits on the router developed by companies such as Linksys, ASUS, MikroTik and D-Link.
The botnet operators used the proxy botnet for various activities such as brute forc, video advertisement fraud, general traffic obfuscation and more.
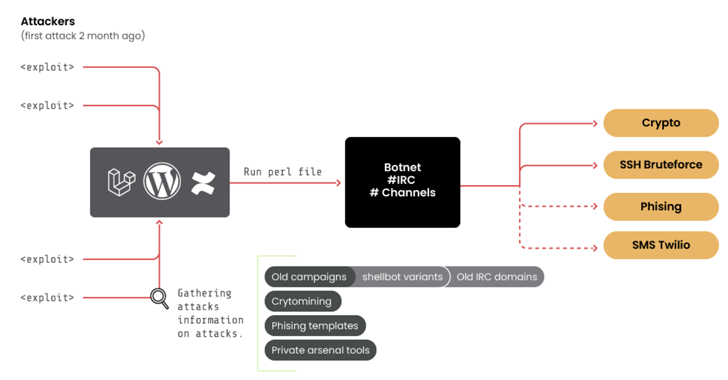
To expand the botnet the threat actor will continuously scan for vulnerable services running on IoT devices and if they detect any vulnerable device it then drops a shell script.
TheMoon botnet targets IoT applications running on port 8080 and the once the dropped shell script executed it downloads the initial stages of the payload.
Security researchers from CenturyLink found the new module is different from the previous one, the new module turns the infected device into a SOCKS5 proxy. The new module allows the botnet author to sell its proxy network as a service to others.

CenturyLink discovered that each IP hosted on TCP port 8002 When connecting to this port, a stream of log messages associated with a video advertisement fraud campaign was automatically received.
“One six-hour time period from a single server resulted in requests to 19,000 unique URLs on 2,700 unique domains. After browsing some of the URLs, it was apparent they all had embedded YouTube videos.”
The IP key has a base64 encoded string and it represents the proxy used for the video ad fraud request.

Centurylink blocked the TheMoon infrastructure on it’s ISP network and it notified another other network operators to potentially block the infected devices. Further details and IoC can be found in Century link report.
“The always-on nature of IoT devices and the ability to masquerade as normal home users make broadband networks prime targets for these types of attacks,” reads CenturyLink report.
Related Read