Qualcomm recently issued warnings about three zero-day vulnerabilities within its GPU and Compute DSP drivers that are currently being exploited by hackers. These warnings were initiated based on information received from Google’s Threat Analysis Group (TAG) and Project Zero teams. According to their reports, there is limited but targeted exploitation of vulnerabilities identified as CVE-2023-33106, CVE-2023-33107, CVE-2022-22071, and CVE-2023-33063.
In response to these imminent threats, Qualcomm has rolled out security updates designed to rectify the issues present within its Adreno GPU and Compute DSP drivers. The company has promptly communicated this information to the affected Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs), urging them to implement these security updates without delay.
One of the significant flaws, CVE-2022-22071, which was initially disclosed in May 2022, is categorized as a high-severity issue, with a CVSS v3.1 score of 8.4. This vulnerability is a use-after-free bug that can be exploited locally and affects widely-used chips, including the SD855, SD865 5G, and SD888 5G.
However, Qualcomm has opted to remain tight-lipped regarding the details of the other actively exploited vulnerabilities, namely CVE-2023-33106, CVE-2022-22071, and CVE-2023-33063. Further information on these vulnerabilities is expected to be disclosed in the company’s security bulletin scheduled for December 2023.
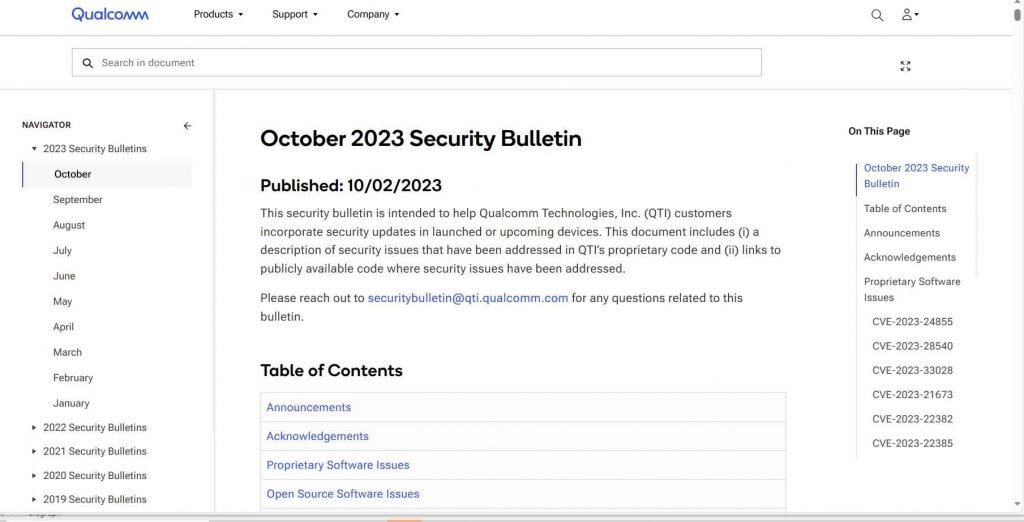
In addition to these, Qualcomm’s recent security bulletin also shed light on three other critical vulnerabilities, each with severe implications:
- CVE-2023-24855 involves memory corruption within Qualcomm’s Modem component. This occurs when processing security-related configurations prior to the AS Security Exchange and has a CVSS v3.1 score of 9.8.
- CVE-2023-28540 relates to a cryptographic issue within the Data Modem component, resulting from insufficient authentication processes during TLS handshakes, with a CVSS v3.1 score of 9.1.
- CVE-2023-33028 involves memory corruption in the WLAN firmware which occurs during the copying of pmk cache memory without conducting necessary size checks, and it holds a CVSS v3.1 score of 9.8.
In light of these findings, Qualcomm disclosed an additional 13 high-severity flaws along with three more vulnerabilities classified as critical, all of which were identified by the company’s engineers. In total, Qualcomm has released updates to address 17 vulnerabilities across various components while highlighting that three zero-day vulnerabilities are currently being actively exploited.
Of these identified vulnerabilities, three have been classified as critical, 13 are high-severity, and one is medium-severity. Qualcomm’s advisory noted: “There are indications from Google Threat Analysis Group and Google Project Zero that CVE-2023-33106, CVE-2023-33107, CVE-2022-22071, and CVE-2023-33063 may be under limited, targeted exploitation.”
To safeguard against these vulnerabilities, patches for issues in the Adreno GPU and Compute DSP drivers have been issued and are readily available. OEMs have been duly notified and strongly urged to deploy these security patches at the earliest convenience to prevent potential exploitation.
Users of Qualcomm products are advised to stay vigilant and apply updates provided by OEMs as soon as they are released to ensure their devices are protected from these vulnerabilities. This proactive approach to device security is crucial in mitigating the risk of exploitation and maintaining the integrity and functionality of devices that play a pivotal role in various technological applications.

Information security specialist, currently working as risk infrastructure specialist & investigator.
15 years of experience in risk and control process, security audit support, business continuity design and support, workgroup management and information security standards.