Eaton developers have announced the release of some security patches for their Intelligent Power Manager (IPM) software, hoping to fix some security flaws considered critical, including a couple of bugs that would allow threat actors to disrupt power supply in affected deployments. The IPM solution is designed to ensure system uptime and data integrity by enabling organizations to remotely monitor, manage, and control the uninterrupted power supply (UPS) devices connected to their networks.
According to an alert issued by the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), a total of six IPM flaws reside that could be exploited to deploy SQL injection attacks, arbitrary file deletion, command execution, and remote code execution.
Although the report specifies that some of these flaws can only be exploited by authenticated threat actors, others can be exploited without requiring authentication, triggering in all kinds of risk scenarios.
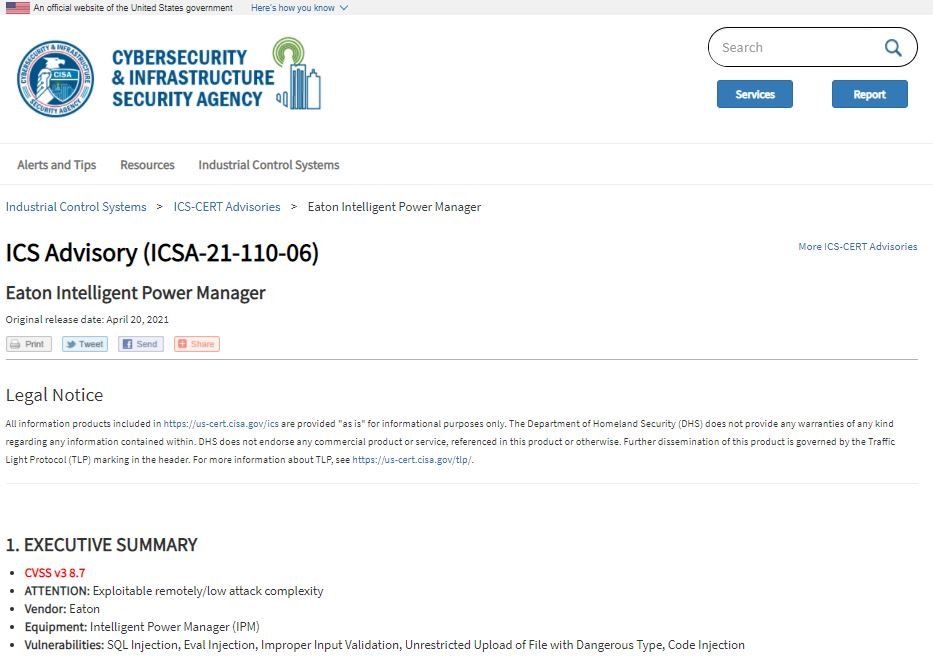
Amir Preminger, a researcher who notified Eaton about these vulnerabilities, mentioned that the issues were identified in an IPM software web server interface that allows users to configure the product. This web server is generally accessible from the local network and is not hosted on public servers.
Security flaws affect running versions of Eaton IPM and Intelligent Power Manager Virtual Appliance (IPM VA) earlier than 1.69, and running versions of Intelligent Power Protector (IPP) earlier than 1.68. Versions 1.69 and 1.68 address vulnerabilities, so users of affected deployments are advised to update as soon as possible. Organizations can also block ports 4679 and 4680 as an alternative method to prevent exploitation.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
He is a well-known expert in mobile security and malware analysis. He studied Computer Science at NYU and started working as a cyber security analyst in 2003. He is actively working as an anti-malware expert. He also worked for security companies like Kaspersky Lab. His everyday job includes researching about new malware and cyber security incidents. Also he has deep level of knowledge in mobile security and mobile vulnerabilities.