AI has slowly become a crucial part of our lives and the segment is continuously booming. However, the process of machine learning is not as environmentally friendly as it was thought to be.
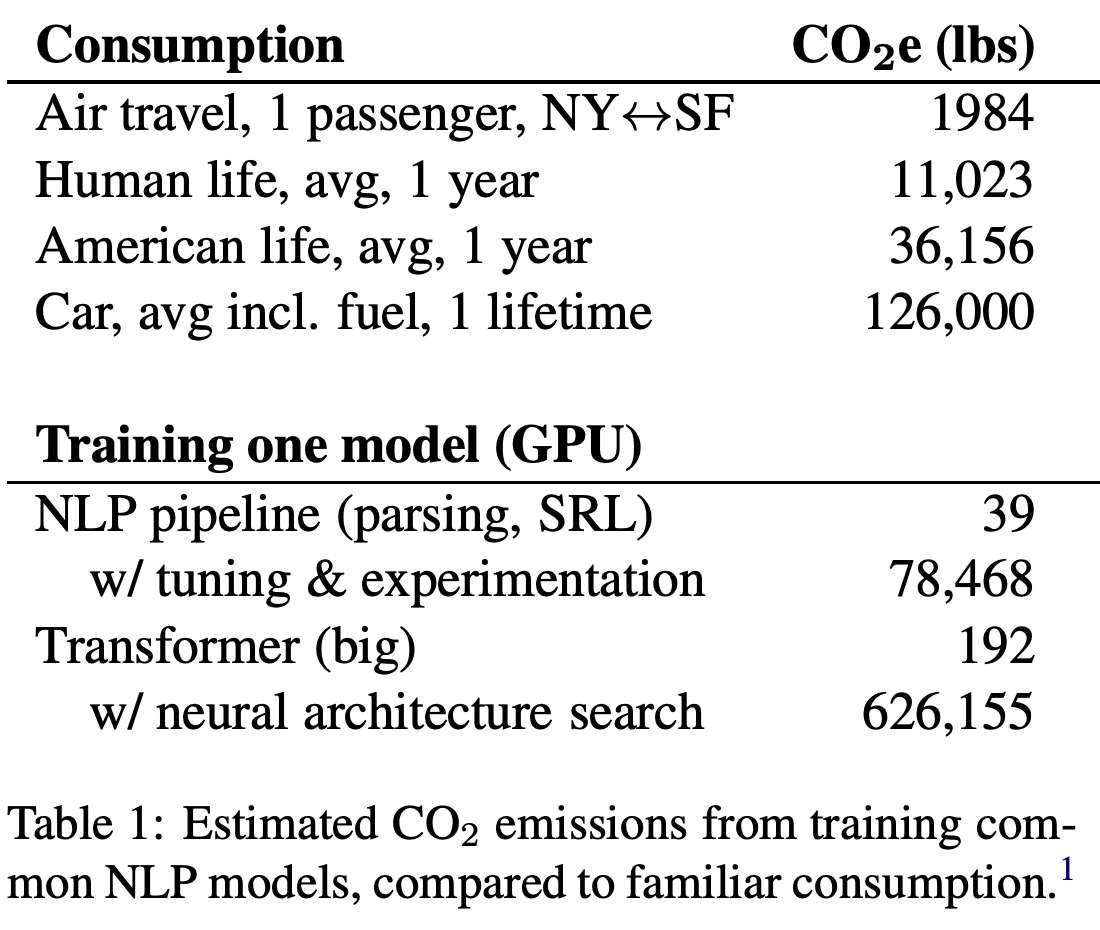
According to media reports, researchers at the University of Massachusetts have found that the process of training various AI models can produce five times more carbon than a car in America. The report states that the amount of carbon dioxide produced during the process is more than 626,000 pounds.
The paper talks about the training process of natural language processing (NLP) models, specifically the Transformer, ELMo, BERT, and GPT-2. The research involved training the models on a single GPU for up to a day.
For those who don’t know, natural processing language is a sub-topic of artificial intelligence and involves teaching machines the human languages. The amount of carbon being produced by this training process is huge and throws light on how AI could deeply impact the environment.
Carlos Gómez-Rodríguez, a computer scientist at the University of A Coruña in Spain, who was not involved in the research, said, “Neither I nor other researchers I’ve discussed them with thought the environmental impact was that substantial.”
Not only does the process of training AI affect the environment adversely, but the process is also an expensive one, with more and more usage of resources in the process.
It is further suggested that training AI models can involve more steps as well and can be an extensive one, which would mean more carbon production.